7: Code Red and Code Red II
The Code Red and Code Red II worms popped up in the summer of 2001. Both worms exploited an operating system vulnerability that was found in machines running Windows 2000 and Windows NT. The vulnerability was a buffer overflow problem, which means when a machine running on these operating systems receives more information than its buffers can handle, it starts to overwrite adjacent memory.
The original Code Red worm initiated a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack on the White House. That means all the computers infected with Code Red tried to contact the Web servers at the White House at the same time, overloading the machines. Source: How stuff works
6: Nimda
In the year 2001 another kind of virus spread throughout the internet which was named Nimda. The virus type was worm; it became the fastest propagating computer virus at the time. In fact, according to TruSecure CTO Peter Tippett, it only took 22 minutes from the moment Nimda hit the Internet to reach the top of the list of reported attacks. The prime targets of Nimda were Internet servers side by side affecting the home PCs. The main purpose was to bring Internet Traffic to a crawl. The Nimda used multiple ways for spreading including e-mail, its multiple travel characteristic made it, spread the virus across multiple servers in record time.
5: SQL Slammer/Sapphire
In the year January 2003, a new Web server virus extends across the Internet. Many computer networks were unsuspecting for the assault, and as a result the virus brought down numerous significant systems. The Bank of America’s ATM service stopped, the city of Seattle suffered outages in 911 services and Continental Airlines had to cancel several flights due to electronic ticketing and check-in errors.
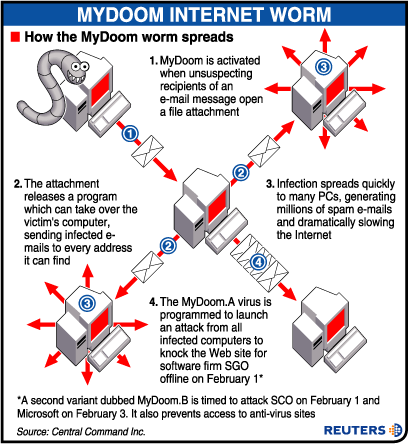
4: MyDoom
The MyDoom virus is an additional worm that can generate a backdoor in the prey computer’s operating system. The original MyDoom virus there have been numerous alternatives had two elicits. One elicit caused the virus to start a refutation of service (DoS) attack starting Feb. 1, 2004. The second elicit controlled the virus to stop issuing itself on Feb. 12, 2004. Even after the virus stopped spreading, the backdoors generated during the first infections remained live.